Low-Latency Ingestion with Datastream
Creation of a near real-time data replication pipeline with a 98% cost reduction.
Context
Developed a Change Data Capture (CDC) data ingestion architecture to replicate data from a transactional database (MySQL) to an analytical environment (BigQuery) in a fast, reliable, and cost-effective manner. The solution was designed to minimize latency and operational costs while offering a robust and scalable approach.
Problem
The previous methodology consumed significant resources from the transactional database, driving up processing costs.
Data loss during replication compromised information integrity and reliability.
Replication time was too slow for large tables, making real-time data analysis unfeasible.
Solution and Contribution
- Architected and implemented a native Google Cloud solution using Datastream, Cloud Storage, Composer (Airflow), and BigQuery.
- Set up CDC binlog capture to export data in Avro format to Cloud Storage.
- Designed a layered architecture — External Tables, Streaming Views, and Raw Tables — ensuring real-time access and optimized batch analysis.
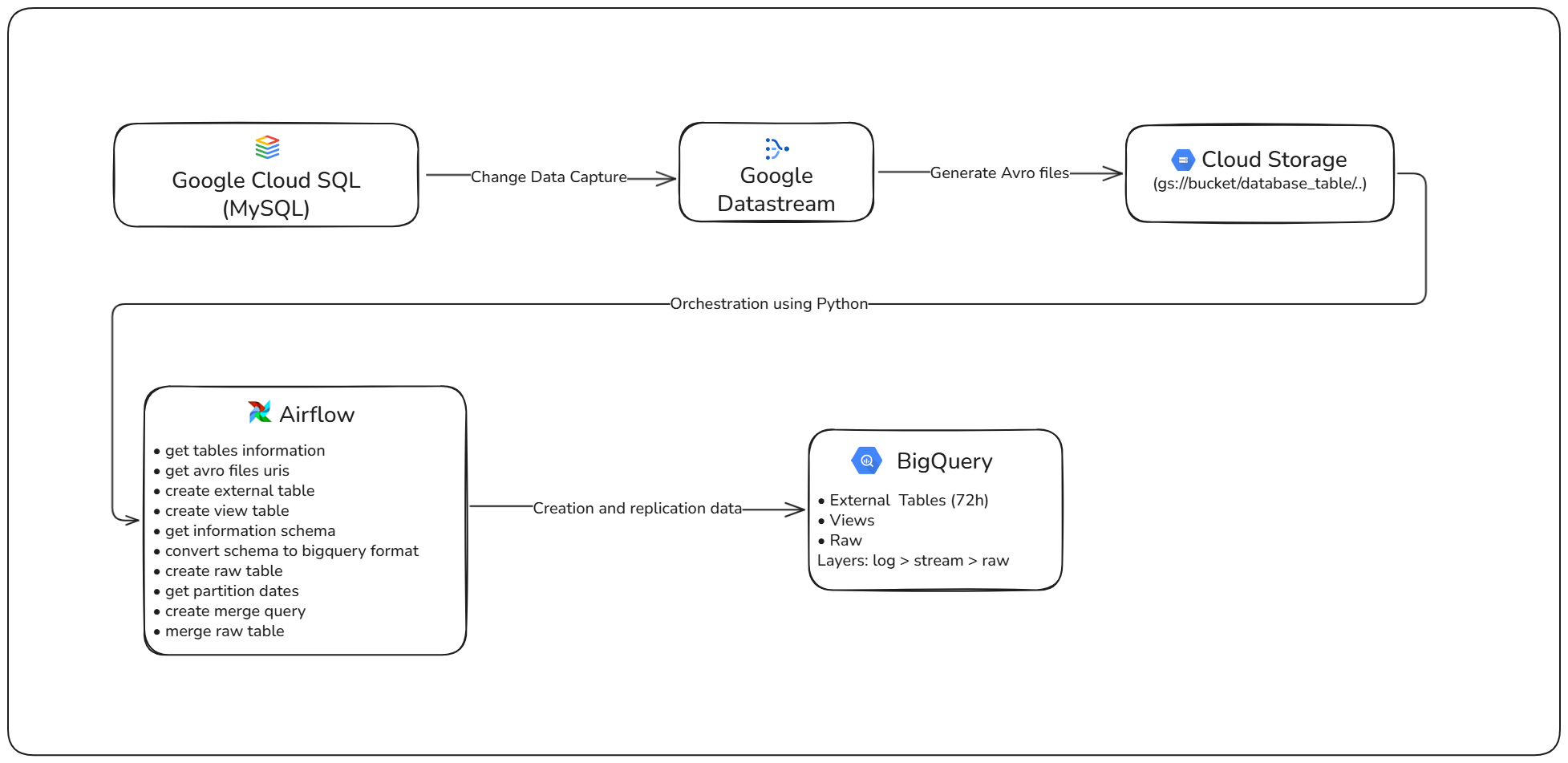

Diagrama de alto nível da arquitetura da solução do Low-Latency Ingestion with Datastream
Results and Impacts
- 98% reduction in data replication costs.
- Data available for analysis within minutes (near real-time) instead of hours.
- Creation of a modular, scalable, and easily replicable ingestion architecture for multiple SaaS clients.
Technologies Used
Technical Details
External Tables and Views Architecture
Datastream writes Avro files directly to Cloud Storage. BigQuery references these files through External Tables, covering data from D-2 to the current day, and builds a View that extracts the latest records. This approach enables querying data updated within 2 minutes with zero processing cost until the query is executed. A `merge select` process then transfers the data to partitioned and clustered Raw Tables, optimizing both cost and query performance. The entire pipeline is orchestrated through a DAG in Cloud Composer (Airflow).